Agentes personalizados¶
Los agentes personalizados proporcionan la máxima flexibilidad en ADK, permitiéndote definir lógica de orquestación arbitraria heredando directamente de BaseAgent e implementando tu propio flujo de control. Esto va más allá de los patrones predefinidos de SequentialAgent, LoopAgent y ParallelAgent, permitiéndote construir flujos de trabajo agénticos altamente específicos y complejos.
Concepto Avanzado
Construir agentes personalizados implementando directamente _run_async_impl (o su equivalente en otros lenguajes) proporciona un control poderoso pero es más complejo que usar los tipos predefinidos LlmAgent o WorkflowAgent estándar. Recomendamos comprender esos tipos de agentes fundamentales primero antes de abordar la lógica de orquestación personalizada.
Introducción: Más Allá de los Flujos de Trabajo Predefinidos¶
¿Qué es un Agente Personalizado?¶
Un Agente Personalizado es esencialmente cualquier clase que crees que hereda de google.adk.agents.BaseAgent e implementa su lógica de ejecución central dentro del método asíncrono _run_async_impl. Tienes control completo sobre cómo este método llama a otros agentes (sub-agentes), gestiona el estado y maneja eventos.
Note
El nombre específico del método para implementar la lógica asíncrona central de un agente puede variar ligeramente según el lenguaje del SDK (por ejemplo, runAsyncImpl en Java, _run_async_impl en Python, o runAsyncImpl en TypeScript). Consulta la documentación de la API específica del lenguaje para más detalles.
¿Por Qué Usarlos?¶
Mientras que los Agentes de Flujo de Trabajo estándar (SequentialAgent, LoopAgent, ParallelAgent) cubren patrones de orquestación comunes, necesitarás un agente Personalizado cuando tus requisitos incluyan:
- Lógica Condicional: Ejecutar diferentes sub-agentes o tomar diferentes rutas basándose en condiciones en tiempo de ejecución o los resultados de pasos anteriores.
- Gestión de Estado Compleja: Implementar lógica intrincada para mantener y actualizar el estado a lo largo del flujo de trabajo más allá del simple paso secuencial.
- Integraciones Externas: Incorporar llamadas a APIs externas, bases de datos o bibliotecas personalizadas directamente dentro del control de flujo de orquestación.
- Selección Dinámica de Agentes: Elegir qué sub-agente(s) ejecutar a continuación basándose en la evaluación dinámica de la situación o entrada.
- Patrones de Flujo de Trabajo Únicos: Implementar lógica de orquestación que no se ajusta a las estructuras estándar secuenciales, paralelas o de bucle.
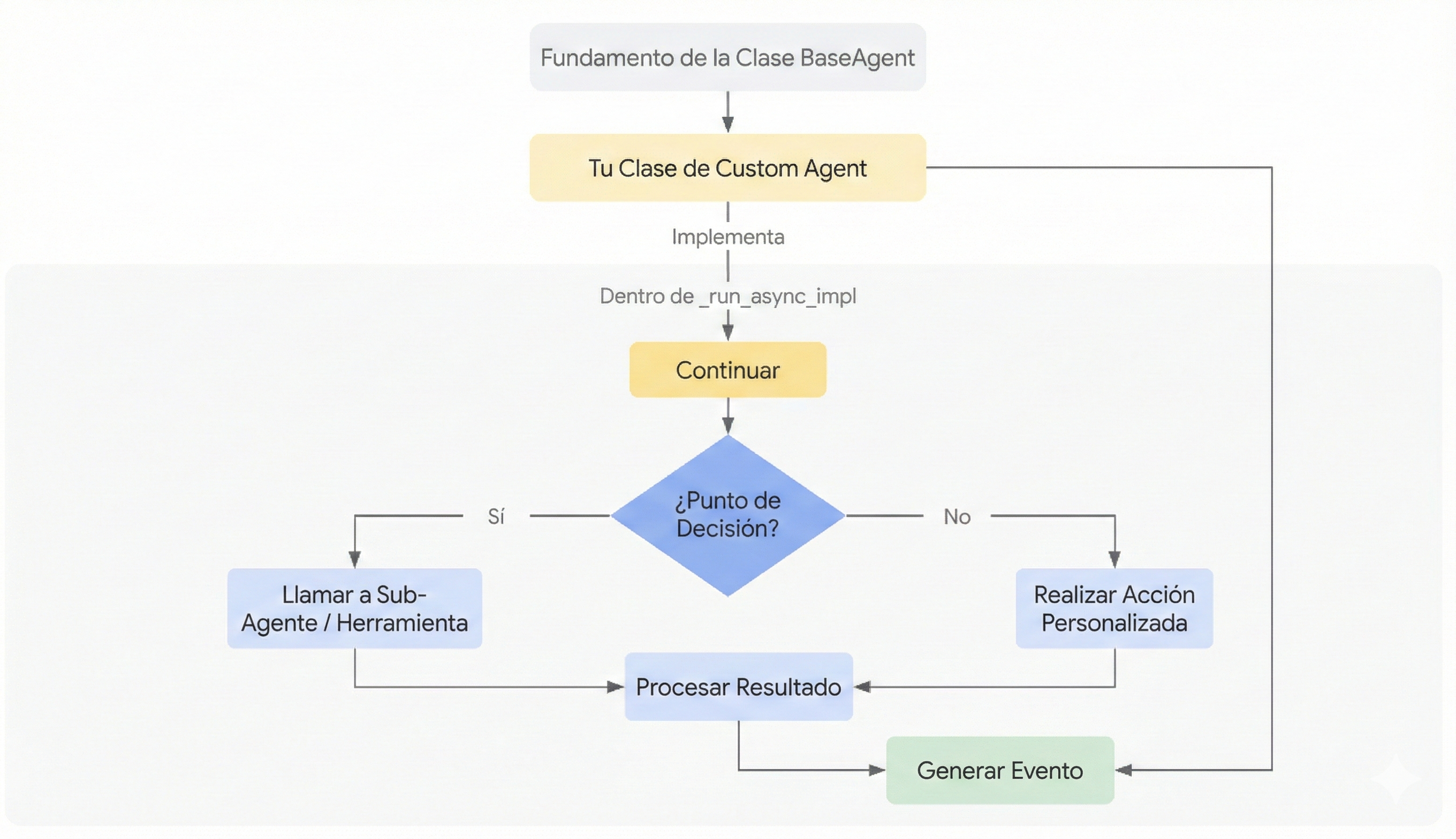
Implementando Lógica Personalizada:¶
El núcleo de cualquier agente personalizado es el método donde defines su comportamiento asíncrono único. Este método te permite orquestar sub-agentes y gestionar el flujo de ejecución.
El corazón de cualquier agente personalizado es el método _run_async_impl. Aquí es donde defines su comportamiento único.
- Firma:
async def _run_async_impl(self, ctx: InvocationContext) -> AsyncGenerator[Event, None]: - Generador Asíncrono: Debe ser una función
async defy retornar unAsyncGenerator. Esto le permite haceryieldde eventos producidos por sub-agentes o su propia lógica de vuelta al ejecutor. ctx(InvocationContext): Proporciona acceso a información crucial en tiempo de ejecución, más importante aúnctx.session.state, que es la forma principal de compartir datos entre pasos orquestados por tu agente personalizado.
El corazón de cualquier agente personalizado es el método runAsyncImpl. Aquí es donde defines su comportamiento único.
- Firma:
async* runAsyncImpl(ctx: InvocationContext): AsyncGenerator<Event, void, undefined> - Generador Asíncrono: Debe ser una función generadora
async(async*). ctx(InvocationContext): Proporciona acceso a información crucial en tiempo de ejecución, más importante aúnctx.session.state, que es la forma principal de compartir datos entre pasos orquestados por tu agente personalizado.
En Go, implementas el método Run como parte de una estructura que satisface la interfaz agent.Agent. La lógica real es típicamente un método en la estructura de tu agente personalizado.
- Firma:
Run(ctx agent.InvocationContext) iter.Seq2[*session.Event, error] - Iterador: El método
Runretorna un iterador (iter.Seq2) que produce eventos y errores. Esta es la forma estándar de manejar resultados en streaming de la ejecución de un agente. ctx(InvocationContext): Elagent.InvocationContextproporciona acceso a la sesión, incluyendo el estado, y otra información crucial en tiempo de ejecución.- Estado de la Sesión: Puedes acceder al estado de la sesión a través de
ctx.Session().State().
El corazón de cualquier agente personalizado es el método runAsyncImpl, que sobrescribes desde BaseAgent.
- Firma:
protected Flowable<Event> runAsyncImpl(InvocationContext ctx) - Flujo Reactivo (
Flowable): Debe retornar unio.reactivex.rxjava3.core.Flowable<Event>. EsteFlowablerepresenta un flujo de eventos que será producido por la lógica del agente personalizado, a menudo combinando o transformando múltiplesFlowablede sub-agentes. ctx(InvocationContext): Proporciona acceso a información crucial en tiempo de ejecución, más importante aúnctx.session().state(), que es unjava.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap<String, Object>. Esta es la forma principal de compartir datos entre pasos orquestados por tu agente personalizado.
Capacidades Clave dentro del Método Asíncrono Central:
-
Llamando a Sub-Agentes: Invocas sub-agentes (que típicamente se almacenan como atributos de instancia como
self.my_llm_agent) usando su métodorun_asyncy haces yield de sus eventos: -
Gestionando el Estado: Lee y escribe en el diccionario de estado de la sesión (
ctx.session.state) para pasar datos entre llamadas a sub-agentes o tomar decisiones:# Leer datos establecidos por un agente anterior previous_result = ctx.session.state.get("some_key") # Tomar una decisión basada en el estado if previous_result == "some_value": # ... llamar a un sub-agente específico ... else: # ... llamar a otro sub-agente ... # Almacenar un resultado para un paso posterior (a menudo hecho a través del output_key de un sub-agente) # ctx.session.state["my_custom_result"] = "calculated_value" -
Implementando Flujo de Control: Usa construcciones estándar de Python (
if/elif/else, buclesfor/while,try/except) para crear flujos de trabajo sofisticados, condicionales o iterativos que involucren tus sub-agentes.
-
Llamando a Sub-Agentes: Invocas sub-agentes (que típicamente se almacenan como propiedades de instancia como
this.myLlmAgent) usando su métodoruny haces yield de sus eventos: -
Gestionando el Estado: Lee y escribe en el objeto de estado de la sesión (
ctx.session.state) para pasar datos entre llamadas a sub-agentes o tomar decisiones:// Leer datos establecidos por un agente anterior const previousResult = ctx.session.state['some_key']; // Tomar una decisión basada en el estado if (previousResult === 'some_value') { // ... llamar a un sub-agente específico ... } else { // ... llamar a otro sub-agente ... } // Almacenar un resultado para un paso posterior (a menudo hecho a través del outputKey de un sub-agente) // ctx.session.state['my_custom_result'] = 'calculated_value'; -
Implementando Flujo de Control: Usa construcciones estándar de TypeScript/JavaScript (
if/else, buclesfor/while,try/catch) para crear flujos de trabajo sofisticados, condicionales o iterativos que involucren tus sub-agentes.
-
Llamando a Sub-Agentes: Invocas sub-agentes llamando a su método
Run. -
Gestionando el Estado: Lee y escribe en el estado de la sesión para pasar datos entre llamadas a sub-agentes o tomar decisiones.
// El `ctx` (`agent.InvocationContext`) se pasa directamente a la función `Run` de tu agente. // Leer datos establecidos por un agente anterior previousResult, err := ctx.Session().State().Get("some_key") if err != nil { // Manejar casos donde la clave podría no existir aún } // Tomar una decisión basada en el estado if val, ok := previousResult.(string); ok && val == "some_value" { // ... llamar a un sub-agente específico ... } else { // ... llamar a otro sub-agente ... } // Almacenar un resultado para un paso posterior if err := ctx.Session().State().Set("my_custom_result", "calculated_value"); err != nil { // Manejar error } -
Implementando Flujo de Control: Usa construcciones estándar de Go (
if/else, buclesfor/switch, goroutines, canales) para crear flujos de trabajo sofisticados, condicionales o iterativos que involucren tus sub-agentes.
-
Llamando a Sub-Agentes: Invocas sub-agentes (que típicamente se almacenan como atributos de instancia u objetos) usando su método de ejecución asíncrono y retornas sus flujos de eventos:
Típicamente encadenas
Flowables de sub-agentes usando operadores de RxJava comoconcatWith,flatMapPublisheroconcatArray.El// Ejemplo: Ejecutando un sub-agente // return someSubAgent.runAsync(ctx); // Ejemplo: Ejecutando sub-agentes secuencialmente Flowable<Event> firstAgentEvents = someSubAgent1.runAsync(ctx) .doOnNext(event -> System.out.println("Event from agent 1: " + event.id())); Flowable<Event> secondAgentEvents = Flowable.defer(() -> someSubAgent2.runAsync(ctx) .doOnNext(event -> System.out.println("Event from agent 2: " + event.id())) ); return firstAgentEvents.concatWith(secondAgentEvents);Flowable.defer()se usa a menudo para etapas subsiguientes si su ejecución depende de la finalización o estado después de etapas previas. -
Gestionando el Estado: Lee y escribe en el estado de la sesión para pasar datos entre llamadas a sub-agentes o tomar decisiones. El estado de la sesión es un
java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap<String, Object>obtenido mediantectx.session().state().// Leer datos establecidos por un agente anterior Object previousResult = ctx.session().state().get("some_key"); // Tomar una decisión basada en el estado if ("some_value".equals(previousResult)) { // ... lógica para incluir el Flowable de un sub-agente específico ... } else { // ... lógica para incluir el Flowable de otro sub-agente ... } // Almacenar un resultado para un paso posterior (a menudo hecho a través del output_key de un sub-agente) // ctx.session().state().put("my_custom_result", "calculated_value"); -
Implementando Flujo de Control: Usa construcciones estándar del lenguaje (
if/else, bucles,try/catch) combinadas con operadores reactivos (RxJava) para crear flujos de trabajo sofisticados.- Condicional:
Flowable.defer()para elegir a quéFlowablesuscribirse basándose en una condición, ofilter()si estás filtrando eventos dentro de un flujo. - Iterativo: Operadores como
repeat(),retry(), o estructurando tu cadenaFlowablepara llamar recursivamente partes de sí misma basándose en condiciones (a menudo gestionado conflatMapPublisheroconcatMap).
- Condicional:
Gestionando Sub-Agentes y Estado¶
Típicamente, un agente personalizado orquesta otros agentes (como LlmAgent, LoopAgent, etc.).
- Inicialización: Usualmente pasas instancias de estos sub-agentes al constructor de tu agente personalizado y los almacenas como campos/atributos de instancia (por ejemplo,
this.story_generator = story_generator_instanceoself.story_generator = story_generator_instance). Esto los hace accesibles dentro de la lógica de ejecución asíncrona central del agente personalizado (como el método_run_async_impl). - Lista de Sub Agentes: Al inicializar el
BaseAgentusando su constructorsuper(), debes pasar una lista desub agents. Esta lista le dice al framework ADK sobre los agentes que son parte de la jerarquía inmediata de este agente personalizado. Es importante para características del framework como gestión del ciclo de vida, introspección y potencialmente capacidades de enrutamiento futuras, incluso si tu lógica de ejecución central (_run_async_impl) llama a los agentes directamente a través deself.xxx_agent. Incluye los agentes que tu lógica personalizada invoca directamente en el nivel superior. - Estado: Como se mencionó,
ctx.session.statees la forma estándar en que los sub-agentes (especialmenteLlmAgents usandooutput key) comunican resultados de vuelta al orquestador y cómo el orquestador pasa las entradas necesarias hacia abajo.
Ejemplo de Patrón de Diseño: StoryFlowAgent¶
Ilustremos el poder de los agentes personalizados con un ejemplo de patrón: un flujo de trabajo de generación de contenido multi-etapa con lógica condicional.
Objetivo: Crear un sistema que genere una historia, la refine iterativamente a través de crítica y revisión, realice verificaciones finales y, crucialmente, regenere la historia si la verificación de tono final falla.
¿Por Qué Personalizado? El requisito central que impulsa la necesidad de un agente personalizado aquí es la regeneración condicional basada en la verificación de tono. Los agentes de flujo de trabajo estándar no tienen ramificación condicional incorporada basada en el resultado de la tarea de un sub-agente. Necesitamos lógica personalizada (if tone == "negative": ...) dentro del orquestador.
Parte 1: Inicialización simplificada del agente personalizado¶
Definimos el StoryFlowAgent heredando de BaseAgent. En __init__, almacenamos los sub-agentes necesarios (pasados) como atributos de instancia y le decimos al framework BaseAgent sobre los agentes de nivel superior que este agente personalizado orquestará directamente.
class StoryFlowAgent(BaseAgent):
"""
Custom agent for a story generation and refinement workflow.
This agent orchestrates a sequence of LLM agents to generate a story,
critique it, revise it, check grammar and tone, and potentially
regenerate the story if the tone is negative.
"""
# --- Field Declarations for Pydantic ---
# Declare the agents passed during initialization as class attributes with type hints
story_generator: LlmAgent
critic: LlmAgent
reviser: LlmAgent
grammar_check: LlmAgent
tone_check: LlmAgent
loop_agent: LoopAgent
sequential_agent: SequentialAgent
# model_config allows setting Pydantic configurations if needed, e.g., arbitrary_types_allowed
model_config = {"arbitrary_types_allowed": True}
def __init__(
self,
name: str,
story_generator: LlmAgent,
critic: LlmAgent,
reviser: LlmAgent,
grammar_check: LlmAgent,
tone_check: LlmAgent,
):
"""
Initializes the StoryFlowAgent.
Args:
name: The name of the agent.
story_generator: An LlmAgent to generate the initial story.
critic: An LlmAgent to critique the story.
reviser: An LlmAgent to revise the story based on criticism.
grammar_check: An LlmAgent to check the grammar.
tone_check: An LlmAgent to analyze the tone.
"""
# Create internal agents *before* calling super().__init__
loop_agent = LoopAgent(
name="CriticReviserLoop", sub_agents=[critic, reviser], max_iterations=2
)
sequential_agent = SequentialAgent(
name="PostProcessing", sub_agents=[grammar_check, tone_check]
)
# Define the sub_agents list for the framework
sub_agents_list = [
story_generator,
loop_agent,
sequential_agent,
]
# Pydantic will validate and assign them based on the class annotations.
super().__init__(
name=name,
story_generator=story_generator,
critic=critic,
reviser=reviser,
grammar_check=grammar_check,
tone_check=tone_check,
loop_agent=loop_agent,
sequential_agent=sequential_agent,
sub_agents=sub_agents_list, # Pass the sub_agents list directly
)
Definimos el StoryFlowAgent extendiendo BaseAgent. En su constructor:
1. Creamos cualquier agente compuesto interno (como LoopAgent o SequentialAgent).
2. Pasamos la lista de todos los sub-agentes de nivel superior al constructor super().
3. Almacenamos los sub-agentes (pasados o creados internamente) como propiedades de instancia (por ejemplo, this.storyGenerator) para que puedan ser accedidos en la lógica runImpl personalizada.
class StoryFlowAgent extends BaseAgent {
// --- Property Declarations for TypeScript ---
private storyGenerator: LlmAgent;
private critic: LlmAgent;
private reviser: LlmAgent;
private grammarCheck: LlmAgent;
private toneCheck: LlmAgent;
private loopAgent: LoopAgent;
private sequentialAgent: SequentialAgent;
constructor(
name: string,
storyGenerator: LlmAgent,
critic: LlmAgent,
reviser: LlmAgent,
grammarCheck: LlmAgent,
toneCheck: LlmAgent
) {
// Create internal composite agents
const loopAgent = new LoopAgent({
name: "CriticReviserLoop",
subAgents: [critic, reviser],
maxIterations: 2,
});
const sequentialAgent = new SequentialAgent({
name: "PostProcessing",
subAgents: [grammarCheck, toneCheck],
});
// Define the sub-agents for the framework to know about
const subAgentsList = [
storyGenerator,
loopAgent,
sequentialAgent,
];
// Call the parent constructor
super({
name,
subAgents: subAgentsList,
});
// Assign agents to class properties for use in the custom run logic
this.storyGenerator = storyGenerator;
this.critic = critic;
this.reviser = reviser;
this.grammarCheck = grammarCheck;
this.toneCheck = toneCheck;
this.loopAgent = loopAgent;
this.sequentialAgent = sequentialAgent;
}
Definimos la estructura StoryFlowAgent y un constructor. En el constructor, almacenamos los sub-agentes necesarios y le decimos al framework BaseAgent sobre los agentes de nivel superior que este agente personalizado orquestará directamente.
// StoryFlowAgent is a custom agent that orchestrates a story generation workflow.
// It encapsulates the logic of running sub-agents in a specific sequence.
type StoryFlowAgent struct {
storyGenerator agent.Agent
revisionLoopAgent agent.Agent
postProcessorAgent agent.Agent
}
// NewStoryFlowAgent creates and configures the entire custom agent workflow.
// It takes individual LLM agents as input and internally creates the necessary
// workflow agents (loop, sequential), returning the final orchestrator agent.
func NewStoryFlowAgent(
storyGenerator,
critic,
reviser,
grammarCheck,
toneCheck agent.Agent,
) (agent.Agent, error) {
loopAgent, err := loopagent.New(loopagent.Config{
MaxIterations: 2,
AgentConfig: agent.Config{
Name: "CriticReviserLoop",
SubAgents: []agent.Agent{critic, reviser},
},
})
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to create loop agent: %w", err)
}
sequentialAgent, err := sequentialagent.New(sequentialagent.Config{
AgentConfig: agent.Config{
Name: "PostProcessing",
SubAgents: []agent.Agent{grammarCheck, toneCheck},
},
})
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to create sequential agent: %w", err)
}
// The StoryFlowAgent struct holds the agents needed for the Run method.
orchestrator := &StoryFlowAgent{
storyGenerator: storyGenerator,
revisionLoopAgent: loopAgent,
postProcessorAgent: sequentialAgent,
}
// agent.New creates the final agent, wiring up the Run method.
return agent.New(agent.Config{
Name: "StoryFlowAgent",
Description: "Orchestrates story generation, critique, revision, and checks.",
SubAgents: []agent.Agent{storyGenerator, loopAgent, sequentialAgent},
Run: orchestrator.Run,
})
}
Definimos el StoryFlowAgentExample extendiendo BaseAgent. En su constructor, almacenamos las instancias de sub-agentes necesarias (pasadas como parámetros) como campos de instancia. Estos sub-agentes de nivel superior, que este agente personalizado orquestará directamente, también se pasan al constructor super de BaseAgent como una lista.
private final LlmAgent storyGenerator;
private final LoopAgent loopAgent;
private final SequentialAgent sequentialAgent;
public StoryFlowAgentExample(
String name, LlmAgent storyGenerator, LoopAgent loopAgent, SequentialAgent sequentialAgent) {
super(
name,
"Orchestrates story generation, critique, revision, and checks.",
List.of(storyGenerator, loopAgent, sequentialAgent),
null,
null);
this.storyGenerator = storyGenerator;
this.loopAgent = loopAgent;
this.sequentialAgent = sequentialAgent;
}
Parte 2: Definiendo la Lógica de Ejecución Personalizada¶
Este método orquesta los sub-agentes usando async/await estándar de Python y flujo de control.
@override
async def _run_async_impl(
self, ctx: InvocationContext
) -> AsyncGenerator[Event, None]:
"""
Implements the custom orchestration logic for the story workflow.
Uses the instance attributes assigned by Pydantic (e.g., self.story_generator).
"""
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Starting story generation workflow.")
# 1. Initial Story Generation
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Running StoryGenerator...")
async for event in self.story_generator.run_async(ctx):
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Event from StoryGenerator: {event.model_dump_json(indent=2, exclude_none=True)}")
yield event
# Check if story was generated before proceeding
if "current_story" not in ctx.session.state or not ctx.session.state["current_story"]:
logger.error(f"[{self.name}] Failed to generate initial story. Aborting workflow.")
return # Stop processing if initial story failed
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Story state after generator: {ctx.session.state.get('current_story')}")
# 2. Critic-Reviser Loop
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Running CriticReviserLoop...")
# Use the loop_agent instance attribute assigned during init
async for event in self.loop_agent.run_async(ctx):
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Event from CriticReviserLoop: {event.model_dump_json(indent=2, exclude_none=True)}")
yield event
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Story state after loop: {ctx.session.state.get('current_story')}")
# 3. Sequential Post-Processing (Grammar and Tone Check)
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Running PostProcessing...")
# Use the sequential_agent instance attribute assigned during init
async for event in self.sequential_agent.run_async(ctx):
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Event from PostProcessing: {event.model_dump_json(indent=2, exclude_none=True)}")
yield event
# 4. Tone-Based Conditional Logic
tone_check_result = ctx.session.state.get("tone_check_result")
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Tone check result: {tone_check_result}")
if tone_check_result == "negative":
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Tone is negative. Regenerating story...")
async for event in self.story_generator.run_async(ctx):
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Event from StoryGenerator (Regen): {event.model_dump_json(indent=2, exclude_none=True)}")
yield event
else:
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Tone is not negative. Keeping current story.")
pass
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Workflow finished.")
- El
story_generatorinicial se ejecuta. Se espera que su salida esté enctx.session.state["current_story"]. - El
loop_agentse ejecuta, que internamente llama alcriticyrevisersecuencialmente pormax_iterationsveces. Leen/escribencurrent_storyycriticismdesde/hacia el estado. - El
sequential_agentse ejecuta, llamando agrammar_checky luegotone_check, leyendocurrent_storyy escribiendogrammar_suggestionsytone_check_resultal estado. - Parte Personalizada: La declaración
ifverifica eltone_check_resultdel estado. Si es "negative", elstory_generatores llamado nuevamente, sobrescribiendo elcurrent_storyen el estado. De lo contrario, el flujo termina.
El método runImpl orquesta los sub-agentes usando async/await estándar de TypeScript y flujo de control. El runLiveImpl también se agrega para manejar escenarios de transmisión en vivo.
// Implements the custom orchestration logic for the story workflow.
async* runLiveImpl(ctx: InvocationContext): AsyncGenerator<Event, void, undefined> {
yield* this.runAsyncImpl(ctx);
}
// Implements the custom orchestration logic for the story workflow.
async* runAsyncImpl(ctx: InvocationContext): AsyncGenerator<Event, void, undefined> {
console.log(`[${this.name}] Starting story generation workflow.`);
// 1. Initial Story Generation
console.log(`[${this.name}] Running StoryGenerator...`);
for await (const event of this.storyGenerator.runAsync(ctx)) {
console.log(`[${this.name}] Event from StoryGenerator: ${JSON.stringify(event, null, 2)}`);
yield event;
}
// Check if the story was generated before proceeding
if (!ctx.session.state["current_story"]) {
console.error(`[${this.name}] Failed to generate initial story. Aborting workflow.`);
return; // Stop processing
}
console.log(`[${this.name}] Story state after generator: ${ctx.session.state['current_story']}`);
// 2. Critic-Reviser Loop
console.log(`[${this.name}] Running CriticReviserLoop...`);
for await (const event of this.loopAgent.runAsync(ctx)) {
console.log(`[${this.name}] Event from CriticReviserLoop: ${JSON.stringify(event, null, 2)}`);
yield event;
}
console.log(`[${this.name}] Story state after loop: ${ctx.session.state['current_story']}`);
// 3. Sequential Post-Processing (Grammar and Tone Check)
console.log(`[${this.name}] Running PostProcessing...`);
for await (const event of this.sequentialAgent.runAsync(ctx)) {
console.log(`[${this.name}] Event from PostProcessing: ${JSON.stringify(event, null, 2)}`);
yield event;
}
// 4. Tone-Based Conditional Logic
const toneCheckResult = ctx.session.state["tone_check_result"] as string;
console.log(`[${this.name}] Tone check result: ${toneCheckResult}`);
if (toneCheckResult === "negative") {
console.log(`[${this.name}] Tone is negative. Regenerating story...`);
for await (const event of this.storyGenerator.runAsync(ctx)) {
console.log(`[${this.name}] Event from StoryGenerator (Regen): ${JSON.stringify(event, null, 2)}`);
yield event;
}
} else {
console.log(`[${this.name}] Tone is not negative. Keeping current story.`);
}
console.log(`[${this.name}] Workflow finished.`);
}
- El
storyGeneratorinicial se ejecuta. Se espera que su salida esté enctx.session.state['current_story']. - El
loopAgentse ejecuta, que internamente llama alcriticyrevisersecuencialmente pormaxIterationsveces. Leen/escribencurrent_storyycriticismdesde/hacia el estado. - El
sequentialAgentse ejecuta, llamando agrammarChecky luegotoneCheck, leyendocurrent_storyy escribiendogrammar_suggestionsytone_check_resultal estado. - Parte Personalizada: La declaración
ifverifica eltone_check_resultdel estado. Si es "negative", elstoryGeneratores llamado nuevamente, sobrescribiendo elcurrent_storyen el estado. De lo contrario, el flujo termina.
El método Run orquesta los sub-agentes llamando a sus respectivos métodos Run en un bucle y haciendo yield de sus eventos.
// Run defines the custom execution logic for the StoryFlowAgent.
func (s *StoryFlowAgent) Run(ctx agent.InvocationContext) iter.Seq2[*session.Event, error] {
return func(yield func(*session.Event, error) bool) {
// Stage 1: Initial Story Generation
for event, err := range s.storyGenerator.Run(ctx) {
if err != nil {
yield(nil, fmt.Errorf("story generator failed: %w", err))
return
}
if !yield(event, nil) {
return
}
}
// Check if story was generated before proceeding
currentStory, err := ctx.Session().State().Get("current_story")
if err != nil || currentStory == "" {
log.Println("Failed to generate initial story. Aborting workflow.")
return
}
// Stage 2: Critic-Reviser Loop
for event, err := range s.revisionLoopAgent.Run(ctx) {
if err != nil {
yield(nil, fmt.Errorf("loop agent failed: %w", err))
return
}
if !yield(event, nil) {
return
}
}
// Stage 3: Post-Processing
for event, err := range s.postProcessorAgent.Run(ctx) {
if err != nil {
yield(nil, fmt.Errorf("sequential agent failed: %w", err))
return
}
if !yield(event, nil) {
return
}
}
// Stage 4: Conditional Regeneration
toneResult, err := ctx.Session().State().Get("tone_check_result")
if err != nil {
log.Printf("Could not read tone_check_result from state: %v. Assuming tone is not negative.", err)
return
}
if tone, ok := toneResult.(string); ok && tone == "negative" {
log.Println("Tone is negative. Regenerating story...")
for event, err := range s.storyGenerator.Run(ctx) {
if err != nil {
yield(nil, fmt.Errorf("story regeneration failed: %w", err))
return
}
if !yield(event, nil) {
return
}
}
} else {
log.Println("Tone is not negative. Keeping current story.")
}
}
}
- El
storyGeneratorinicial se ejecuta. Se espera que su salida esté en el estado de la sesión bajo la clave"current_story". - El
revisionLoopAgentse ejecuta, que internamente llama alcriticyrevisersecuencialmente pormax_iterationsveces. Leen/escribencurrent_storyycriticismdesde/hacia el estado. - El
postProcessorAgentse ejecuta, llamando agrammar_checky luegotone_check, leyendocurrent_storyy escribiendogrammar_suggestionsytone_check_resultal estado. - Parte Personalizada: El código verifica el
tone_check_resultdel estado. Si es "negative", elstory_generatores llamado nuevamente, sobrescribiendo elcurrent_storyen el estado. De lo contrario, el flujo termina.
El método runAsyncImpl orquesta los sub-agentes usando flujos Flowable de RxJava y operadores para flujo de control asíncrono.
@Override
protected Flowable<Event> runAsyncImpl(InvocationContext invocationContext) {
// Implements the custom orchestration logic for the story workflow.
// Uses the instance attributes assigned by Pydantic (e.g., self.story_generator).
logger.log(Level.INFO, () -> String.format("[%s] Starting story generation workflow.", name()));
// Stage 1. Initial Story Generation
Flowable<Event> storyGenFlow = runStage(storyGenerator, invocationContext, "StoryGenerator");
// Stage 2: Critic-Reviser Loop (runs after story generation completes)
Flowable<Event> criticReviserFlow = Flowable.defer(() -> {
if (!isStoryGenerated(invocationContext)) {
logger.log(Level.SEVERE,() ->
String.format("[%s] Failed to generate initial story. Aborting after StoryGenerator.",
name()));
return Flowable.empty(); // Stop further processing if no story
}
logger.log(Level.INFO, () ->
String.format("[%s] Story state after generator: %s",
name(), invocationContext.session().state().get("current_story")));
return runStage(loopAgent, invocationContext, "CriticReviserLoop");
});
// Stage 3: Post-Processing (runs after critic-reviser loop completes)
Flowable<Event> postProcessingFlow = Flowable.defer(() -> {
logger.log(Level.INFO, () ->
String.format("[%s] Story state after loop: %s",
name(), invocationContext.session().state().get("current_story")));
return runStage(sequentialAgent, invocationContext, "PostProcessing");
});
// Stage 4: Conditional Regeneration (runs after post-processing completes)
Flowable<Event> conditionalRegenFlow = Flowable.defer(() -> {
String toneCheckResult = (String) invocationContext.session().state().get("tone_check_result");
logger.log(Level.INFO, () -> String.format("[%s] Tone check result: %s", name(), toneCheckResult));
if ("negative".equalsIgnoreCase(toneCheckResult)) {
logger.log(Level.INFO, () ->
String.format("[%s] Tone is negative. Regenerating story...", name()));
return runStage(storyGenerator, invocationContext, "StoryGenerator (Regen)");
} else {
logger.log(Level.INFO, () ->
String.format("[%s] Tone is not negative. Keeping current story.", name()));
return Flowable.empty(); // No regeneration needed
}
});
return Flowable.concatArray(storyGenFlow, criticReviserFlow, postProcessingFlow, conditionalRegenFlow)
.doOnComplete(() -> logger.log(Level.INFO, () -> String.format("[%s] Workflow finished.", name())));
}
// Helper method for a single agent run stage with logging
private Flowable<Event> runStage(BaseAgent agentToRun, InvocationContext ctx, String stageName) {
logger.log(Level.INFO, () -> String.format("[%s] Running %s...", name(), stageName));
return agentToRun
.runAsync(ctx)
.doOnNext(event ->
logger.log(Level.INFO,() ->
String.format("[%s] Event from %s: %s", name(), stageName, event.toJson())))
.doOnError(err ->
logger.log(Level.SEVERE,
String.format("[%s] Error in %s", name(), stageName), err))
.doOnComplete(() ->
logger.log(Level.INFO, () ->
String.format("[%s] %s finished.", name(), stageName)));
}
- El Flowable inicial
storyGenerator.runAsync(invocationContext)se ejecuta. Se espera que su salida esté eninvocationContext.session().state().get("current_story"). - El Flowable del
loopAgentse ejecuta después (debido aFlowable.concatArrayyFlowable.defer). El LoopAgent internamente llama a los sub-agentescriticyrevisersecuencialmente hastamaxIterations. Leen/escribencurrent_storyycriticismdesde/hacia el estado. - Luego, el Flowable del
sequentialAgentse ejecuta. Llama agrammar_checky luegotone_check, leyendocurrent_storyy escribiendogrammar_suggestionsytone_check_resultal estado. - Parte Personalizada: Después de que el sequentialAgent completa, la lógica dentro de un
Flowable.deferverifica el "tone_check_result" deinvocationContext.session().state(). Si es "negative", el Flowable delstoryGeneratores condicionalmente concatenado y ejecutado nuevamente, sobrescribiendo "current_story". De lo contrario, se usa un Flowable vacío, y el flujo de trabajo general procede a completarse.
Parte 3: Definiendo los Sub-Agentes LLM¶
Estas son definiciones estándar de LlmAgent, responsables de tareas específicas. Su parámetro output key es crucial para colocar resultados en el session.state donde otros agentes o el orquestador personalizado puedan acceder a ellos.
Inyección Directa de Estado en Instrucciones
Observa la instrucción del story_generator. La sintaxis {var} es un marcador de posición. Antes de que la instrucción sea enviada al LLM, el framework ADK reemplaza automáticamente (Ejemplo:{topic}) con el valor de session.state['topic']. Esta es la forma recomendada de proporcionar contexto a un agente, usando plantillas en las instrucciones. Para más detalles, consulta la documentación de Estado.
GEMINI_2_FLASH = "gemini-2.0-flash" # Definir constante de modelo
# --- Define the individual LLM agents ---
story_generator = LlmAgent(
name="StoryGenerator",
model=GEMINI_2_FLASH,
instruction="""You are a story writer. Write a short story (around 100 words), on the following topic: {topic}""",
input_schema=None,
output_key="current_story", # Key for storing output in session state
)
critic = LlmAgent(
name="Critic",
model=GEMINI_2_FLASH,
instruction="""You are a story critic. Review the story provided: {{current_story}}. Provide 1-2 sentences of constructive criticism
on how to improve it. Focus on plot or character.""",
input_schema=None,
output_key="criticism", # Key for storing criticism in session state
)
reviser = LlmAgent(
name="Reviser",
model=GEMINI_2_FLASH,
instruction="""You are a story reviser. Revise the story provided: {{current_story}}, based on the criticism in
{{criticism}}. Output only the revised story.""",
input_schema=None,
output_key="current_story", # Overwrites the original story
)
grammar_check = LlmAgent(
name="GrammarCheck",
model=GEMINI_2_FLASH,
instruction="""You are a grammar checker. Check the grammar of the story provided: {current_story}. Output only the suggested
corrections as a list, or output 'Grammar is good!' if there are no errors.""",
input_schema=None,
output_key="grammar_suggestions",
)
tone_check = LlmAgent(
name="ToneCheck",
model=GEMINI_2_FLASH,
instruction="""You are a tone analyzer. Analyze the tone of the story provided: {current_story}. Output only one word: 'positive' if
the tone is generally positive, 'negative' if the tone is generally negative, or 'neutral'
otherwise.""",
input_schema=None,
output_key="tone_check_result", # This agent's output determines the conditional flow
)
// --- Define the individual LLM agents ---
const storyGenerator = new LlmAgent({
name: "StoryGenerator",
model: GEMINI_MODEL,
instruction: `You are a story writer. Write a short story (around 100 words), on the following topic: {topic}`,
outputKey: "current_story",
});
const critic = new LlmAgent({
name: "Critic",
model: GEMINI_MODEL,
instruction: `You are a story critic. Review the story provided: {{current_story}}. Provide 1-2 sentences of constructive criticism
on how to improve it. Focus on plot or character.`,
outputKey: "criticism",
});
const reviser = new LlmAgent({
name: "Reviser",
model: GEMINI_MODEL,
instruction: `You are a story reviser. Revise the story provided: {{current_story}}, based on the criticism in
{{criticism}}. Output only the revised story.`,
outputKey: "current_story", // Overwrites the original story
});
const grammarCheck = new LlmAgent({
name: "GrammarCheck",
model: GEMINI_MODEL,
instruction: `You are a grammar checker. Check the grammar of the story provided: {current_story}. Output only the suggested
corrections as a list, or output 'Grammar is good!' if there are no errors.`,
outputKey: "grammar_suggestions",
});
const toneCheck = new LlmAgent({
name: "ToneCheck",
model: GEMINI_MODEL,
instruction: `You are a tone analyzer. Analyze the tone of the story provided: {current_story}. Output only one word: 'positive' if
the tone is generally positive, 'negative' if the tone is generally negative, or 'neutral'
otherwise.`,
outputKey: "tone_check_result",
});
// --- Define the individual LLM agents ---
storyGenerator, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "StoryGenerator",
Model: model,
Description: "Generates the initial story.",
Instruction: "You are a story writer. Write a short story (around 100 words) about a cat, based on the topic: {topic}",
OutputKey: "current_story",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create StoryGenerator agent: %v", err)
}
critic, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "Critic",
Model: model,
Description: "Critiques the story.",
Instruction: "You are a story critic. Review the story: {current_story}. Provide 1-2 sentences of constructive criticism on how to improve it. Focus on plot or character.",
OutputKey: "criticism",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create Critic agent: %v", err)
}
reviser, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "Reviser",
Model: model,
Description: "Revises the story based on criticism.",
Instruction: "You are a story reviser. Revise the story: {current_story}, based on the criticism: {criticism}. Output only the revised story.",
OutputKey: "current_story",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create Reviser agent: %v", err)
}
grammarCheck, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "GrammarCheck",
Model: model,
Description: "Checks grammar and suggests corrections.",
Instruction: "You are a grammar checker. Check the grammar of the story: {current_story}. Output only the suggested corrections as a list, or output 'Grammar is good!' if there are no errors.",
OutputKey: "grammar_suggestions",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create GrammarCheck agent: %v", err)
}
toneCheck, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "ToneCheck",
Model: model,
Description: "Analyzes the tone of the story.",
Instruction: "You are a tone analyzer. Analyze the tone of the story: {current_story}. Output only one word: 'positive' if the tone is generally positive, 'negative' if the tone is generally negative, or 'neutral' otherwise.",
OutputKey: "tone_check_result",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create ToneCheck agent: %v", err)
}
// --- Define the individual LLM agents ---
LlmAgent storyGenerator =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("StoryGenerator")
.model(MODEL_NAME)
.description("Generates the initial story.")
.instruction(
"""
You are a story writer. Write a short story (around 100 words) about a cat,
based on the topic: {topic}
""")
.inputSchema(null)
.outputKey("current_story") // Key for storing output in session state
.build();
LlmAgent critic =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("Critic")
.model(MODEL_NAME)
.description("Critiques the story.")
.instruction(
"""
You are a story critic. Review the story: {current_story}. Provide 1-2 sentences of constructive criticism
on how to improve it. Focus on plot or character.
""")
.inputSchema(null)
.outputKey("criticism") // Key for storing criticism in session state
.build();
LlmAgent reviser =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("Reviser")
.model(MODEL_NAME)
.description("Revises the story based on criticism.")
.instruction(
"""
You are a story reviser. Revise the story: {current_story}, based on the criticism: {criticism}. Output only the revised story.
""")
.inputSchema(null)
.outputKey("current_story") // Overwrites the original story
.build();
LlmAgent grammarCheck =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("GrammarCheck")
.model(MODEL_NAME)
.description("Checks grammar and suggests corrections.")
.instruction(
"""
You are a grammar checker. Check the grammar of the story: {current_story}. Output only the suggested
corrections as a list, or output 'Grammar is good!' if there are no errors.
""")
.outputKey("grammar_suggestions")
.build();
LlmAgent toneCheck =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("ToneCheck")
.model(MODEL_NAME)
.description("Analyzes the tone of the story.")
.instruction(
"""
You are a tone analyzer. Analyze the tone of the story: {current_story}. Output only one word: 'positive' if
the tone is generally positive, 'negative' if the tone is generally negative, or 'neutral'
otherwise.
""")
.outputKey("tone_check_result") // This agent's output determines the conditional flow
.build();
LoopAgent loopAgent =
LoopAgent.builder()
.name("CriticReviserLoop")
.description("Iteratively critiques and revises the story.")
.subAgents(critic, reviser)
.maxIterations(2)
.build();
SequentialAgent sequentialAgent =
SequentialAgent.builder()
.name("PostProcessing")
.description("Performs grammar and tone checks sequentially.")
.subAgents(grammarCheck, toneCheck)
.build();
Parte 4: Instanciando y Ejecutando el agente personalizado¶
Finalmente, instancias tu StoryFlowAgent y usas el Runner como de costumbre.
# --- Create the custom agent instance ---
story_flow_agent = StoryFlowAgent(
name="StoryFlowAgent",
story_generator=story_generator,
critic=critic,
reviser=reviser,
grammar_check=grammar_check,
tone_check=tone_check,
)
INITIAL_STATE = {"topic": "a brave kitten exploring a haunted house"}
# --- Setup Runner and Session ---
async def setup_session_and_runner():
session_service = InMemorySessionService()
session = await session_service.create_session(app_name=APP_NAME, user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID, state=INITIAL_STATE)
logger.info(f"Initial session state: {session.state}")
runner = Runner(
agent=story_flow_agent, # Pass the custom orchestrator agent
app_name=APP_NAME,
session_service=session_service
)
return session_service, runner
# --- Function to Interact with the Agent ---
async def call_agent_async(user_input_topic: str):
"""
Sends a new topic to the agent (overwriting the initial one if needed)
and runs the workflow.
"""
session_service, runner = await setup_session_and_runner()
current_session = session_service.sessions[APP_NAME][USER_ID][SESSION_ID]
current_session.state["topic"] = user_input_topic
logger.info(f"Updated session state topic to: {user_input_topic}")
content = types.Content(role='user', parts=[types.Part(text=f"Generate a story about the preset topic.")])
events = runner.run_async(user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID, new_message=content)
final_response = "No final response captured."
async for event in events:
if event.is_final_response() and event.content and event.content.parts:
logger.info(f"Potential final response from [{event.author}]: {event.content.parts[0].text}")
final_response = event.content.parts[0].text
print("\n--- Agent Interaction Result ---")
print("Agent Final Response: ", final_response)
final_session = await session_service.get_session(app_name=APP_NAME,
user_id=USER_ID,
session_id=SESSION_ID)
print("Final Session State:")
import json
print(json.dumps(final_session.state, indent=2))
print("-------------------------------\n")
# --- Run the Agent ---
# Note: In Colab, you can directly use 'await' at the top level.
# If running this code as a standalone Python script, you'll need to use asyncio.run() or manage the event loop.
await call_agent_async("a lonely robot finding a friend in a junkyard")
// --- Create the custom agent instance ---
const storyFlowAgent = new StoryFlowAgent(
"StoryFlowAgent",
storyGenerator,
critic,
reviser,
grammarCheck,
toneCheck
);
const INITIAL_STATE = { "topic": "a brave kitten exploring a haunted house" };
// --- Setup Runner and Session ---
async function setupRunnerAndSession() {
const runner = new InMemoryRunner({
agent: storyFlowAgent,
appName: APP_NAME,
});
const session = await runner.sessionService.createSession({
appName: APP_NAME,
userId: USER_ID,
sessionId: SESSION_ID,
state: INITIAL_STATE,
});
console.log(`Initial session state: ${JSON.stringify(session.state, null, 2)}`);
return runner;
}
// --- Function to Interact with the Agent ---
async function callAgent(runner: InMemoryRunner, userInputTopic: string) {
const currentSession = await runner.sessionService.getSession({
appName: APP_NAME,
userId: USER_ID,
sessionId: SESSION_ID
});
if (!currentSession) {
return;
}
// Update the state with the new topic for this run
currentSession.state["topic"] = userInputTopic;
console.log(`Updated session state topic to: ${userInputTopic}`);
let finalResponse = "No final response captured.";
for await (const event of runner.runAsync({
userId: USER_ID,
sessionId: SESSION_ID,
newMessage: createUserContent(`Generate a story about: ${userInputTopic}`)
})) {
if (isFinalResponse(event) && event.content?.parts?.length) {
console.log(`Potential final response from [${event.author}]: ${event.content.parts.map(part => part.text ?? '').join('')}`);
finalResponse = event.content.parts.map(part => part.text ?? '').join('');
}
}
const finalSession = await runner.sessionService.getSession({
appName: APP_NAME,
userId: USER_ID,
sessionId: SESSION_ID
});
console.log("\n--- Agent Interaction Result ---");
console.log("Agent Final Response: ", finalResponse);
console.log("Final Session State:");
console.log(JSON.stringify(finalSession?.state, null, 2));
console.log("-------------------------------\n");
}
// --- Run the Agent ---
async function main() {
const runner = await setupRunnerAndSession();
await callAgent(runner, "a lonely robot finding a friend in a junkyard");
}
main();
// Instantiate the custom agent, which encapsulates the workflow agents.
storyFlowAgent, err := NewStoryFlowAgent(
storyGenerator,
critic,
reviser,
grammarCheck,
toneCheck,
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create story flow agent: %v", err)
}
// --- Run the Agent ---
sessionService := session.InMemoryService()
initialState := map[string]any{
"topic": "a brave kitten exploring a haunted house",
}
sessionInstance, err := sessionService.Create(ctx, &session.CreateRequest{
AppName: appName,
UserID: userID,
State: initialState,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create session: %v", err)
}
userTopic := "a lonely robot finding a friend in a junkyard"
r, err := runner.New(runner.Config{
AppName: appName,
Agent: storyFlowAgent,
SessionService: sessionService,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create runner: %v", err)
}
input := genai.NewContentFromText("Generate a story about: "+userTopic, genai.RoleUser)
events := r.Run(ctx, userID, sessionInstance.Session.ID(), input, agent.RunConfig{
StreamingMode: agent.StreamingModeSSE,
})
var finalResponse string
for event, err := range events {
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("An error occurred during agent execution: %v", err)
}
for _, part := range event.Content.Parts {
// Accumulate text from all parts of the final response.
finalResponse += part.Text
}
}
fmt.Println("\n--- Agent Interaction Result ---")
fmt.Println("Agent Final Response: " + finalResponse)
finalSession, err := sessionService.Get(ctx, &session.GetRequest{
UserID: userID,
AppName: appName,
SessionID: sessionInstance.Session.ID(),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to retrieve final session: %v", err)
}
fmt.Println("Final Session State:", finalSession.Session.State())
}
// --- Function to Interact with the Agent ---
// Sends a new topic to the agent (overwriting the initial one if needed)
// and runs the workflow.
public static void runAgent(StoryFlowAgentExample agent, String userTopic) {
// --- Setup Runner and Session ---
InMemoryRunner runner = new InMemoryRunner(agent);
Map<String, Object> initialState = new HashMap<>();
initialState.put("topic", "a brave kitten exploring a haunted house");
Session session =
runner
.sessionService()
.createSession(APP_NAME, USER_ID, new ConcurrentHashMap<>(initialState), SESSION_ID)
.blockingGet();
logger.log(Level.INFO, () -> String.format("Initial session state: %s", session.state()));
session.state().put("topic", userTopic); // Update the state in the retrieved session
logger.log(Level.INFO, () -> String.format("Updated session state topic to: %s", userTopic));
Content userMessage = Content.fromParts(Part.fromText("Generate a story about: " + userTopic));
// Use the modified session object for the run
Flowable<Event> eventStream = runner.runAsync(USER_ID, session.id(), userMessage);
final String[] finalResponse = {"No final response captured."};
eventStream.blockingForEach(
event -> {
if (event.finalResponse() && event.content().isPresent()) {
String author = event.author() != null ? event.author() : "UNKNOWN_AUTHOR";
Optional<String> textOpt =
event
.content()
.flatMap(Content::parts)
.filter(parts -> !parts.isEmpty())
.map(parts -> parts.get(0).text().orElse(""));
logger.log(Level.INFO, () ->
String.format("Potential final response from [%s]: %s", author, textOpt.orElse("N/A")));
textOpt.ifPresent(text -> finalResponse[0] = text);
}
});
System.out.println("\n--- Agent Interaction Result ---");
System.out.println("Agent Final Response: " + finalResponse[0]);
// Retrieve session again to see the final state after the run
Session finalSession =
runner
.sessionService()
.getSession(APP_NAME, USER_ID, SESSION_ID, Optional.empty())
.blockingGet();
assert finalSession != null;
System.out.println("Final Session State:" + finalSession.state());
System.out.println("-------------------------------\n");
}
(Nota: El código ejecutable completo, incluyendo imports y lógica de ejecución, se puede encontrar enlazado abajo.)
Ejemplo de Código Completo¶
Storyflow Agent
# Código ejecutable completo para el ejemplo de StoryFlowAgent
# Copyright 2025 Google LLC
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import logging
from typing import AsyncGenerator
from typing_extensions import override
from google.adk.agents import LlmAgent, BaseAgent, LoopAgent, SequentialAgent
from google.adk.agents.invocation_context import InvocationContext
from google.genai import types
from google.adk.sessions import InMemorySessionService
from google.adk.runners import Runner
from google.adk.events import Event
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
# --- Constants ---
APP_NAME = "story_app"
USER_ID = "12345"
SESSION_ID = "123344"
GEMINI_2_FLASH = "gemini-2.0-flash"
# --- Configure Logging ---
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
# --- Custom Orchestrator Agent ---
class StoryFlowAgent(BaseAgent):
"""
Custom agent for a story generation and refinement workflow.
This agent orchestrates a sequence of LLM agents to generate a story,
critique it, revise it, check grammar and tone, and potentially
regenerate the story if the tone is negative.
"""
# --- Field Declarations for Pydantic ---
# Declare the agents passed during initialization as class attributes with type hints
story_generator: LlmAgent
critic: LlmAgent
reviser: LlmAgent
grammar_check: LlmAgent
tone_check: LlmAgent
loop_agent: LoopAgent
sequential_agent: SequentialAgent
# model_config allows setting Pydantic configurations if needed, e.g., arbitrary_types_allowed
model_config = {"arbitrary_types_allowed": True}
def __init__(
self,
name: str,
story_generator: LlmAgent,
critic: LlmAgent,
reviser: LlmAgent,
grammar_check: LlmAgent,
tone_check: LlmAgent,
):
"""
Initializes the StoryFlowAgent.
Args:
name: The name of the agent.
story_generator: An LlmAgent to generate the initial story.
critic: An LlmAgent to critique the story.
reviser: An LlmAgent to revise the story based on criticism.
grammar_check: An LlmAgent to check the grammar.
tone_check: An LlmAgent to analyze the tone.
"""
# Create internal agents *before* calling super().__init__
loop_agent = LoopAgent(
name="CriticReviserLoop", sub_agents=[critic, reviser], max_iterations=2
)
sequential_agent = SequentialAgent(
name="PostProcessing", sub_agents=[grammar_check, tone_check]
)
# Define the sub_agents list for the framework
sub_agents_list = [
story_generator,
loop_agent,
sequential_agent,
]
# Pydantic will validate and assign them based on the class annotations.
super().__init__(
name=name,
story_generator=story_generator,
critic=critic,
reviser=reviser,
grammar_check=grammar_check,
tone_check=tone_check,
loop_agent=loop_agent,
sequential_agent=sequential_agent,
sub_agents=sub_agents_list, # Pass the sub_agents list directly
)
@override
async def _run_async_impl(
self, ctx: InvocationContext
) -> AsyncGenerator[Event, None]:
"""
Implements the custom orchestration logic for the story workflow.
Uses the instance attributes assigned by Pydantic (e.g., self.story_generator).
"""
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Starting story generation workflow.")
# 1. Initial Story Generation
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Running StoryGenerator...")
async for event in self.story_generator.run_async(ctx):
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Event from StoryGenerator: {event.model_dump_json(indent=2, exclude_none=True)}")
yield event
# Check if story was generated before proceeding
if "current_story" not in ctx.session.state or not ctx.session.state["current_story"]:
logger.error(f"[{self.name}] Failed to generate initial story. Aborting workflow.")
return # Stop processing if initial story failed
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Story state after generator: {ctx.session.state.get('current_story')}")
# 2. Critic-Reviser Loop
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Running CriticReviserLoop...")
# Use the loop_agent instance attribute assigned during init
async for event in self.loop_agent.run_async(ctx):
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Event from CriticReviserLoop: {event.model_dump_json(indent=2, exclude_none=True)}")
yield event
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Story state after loop: {ctx.session.state.get('current_story')}")
# 3. Sequential Post-Processing (Grammar and Tone Check)
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Running PostProcessing...")
# Use the sequential_agent instance attribute assigned during init
async for event in self.sequential_agent.run_async(ctx):
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Event from PostProcessing: {event.model_dump_json(indent=2, exclude_none=True)}")
yield event
# 4. Tone-Based Conditional Logic
tone_check_result = ctx.session.state.get("tone_check_result")
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Tone check result: {tone_check_result}")
if tone_check_result == "negative":
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Tone is negative. Regenerating story...")
async for event in self.story_generator.run_async(ctx):
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Event from StoryGenerator (Regen): {event.model_dump_json(indent=2, exclude_none=True)}")
yield event
else:
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Tone is not negative. Keeping current story.")
pass
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Workflow finished.")
# --- Define the individual LLM agents ---
story_generator = LlmAgent(
name="StoryGenerator",
model=GEMINI_2_FLASH,
instruction="""You are a story writer. Write a short story (around 100 words), on the following topic: {topic}""",
input_schema=None,
output_key="current_story", # Key for storing output in session state
)
critic = LlmAgent(
name="Critic",
model=GEMINI_2_FLASH,
instruction="""You are a story critic. Review the story provided: {{current_story}}. Provide 1-2 sentences of constructive criticism
on how to improve it. Focus on plot or character.""",
input_schema=None,
output_key="criticism", # Key for storing criticism in session state
)
reviser = LlmAgent(
name="Reviser",
model=GEMINI_2_FLASH,
instruction="""You are a story reviser. Revise the story provided: {{current_story}}, based on the criticism in
{{criticism}}. Output only the revised story.""",
input_schema=None,
output_key="current_story", # Overwrites the original story
)
grammar_check = LlmAgent(
name="GrammarCheck",
model=GEMINI_2_FLASH,
instruction="""You are a grammar checker. Check the grammar of the story provided: {current_story}. Output only the suggested
corrections as a list, or output 'Grammar is good!' if there are no errors.""",
input_schema=None,
output_key="grammar_suggestions",
)
tone_check = LlmAgent(
name="ToneCheck",
model=GEMINI_2_FLASH,
instruction="""You are a tone analyzer. Analyze the tone of the story provided: {current_story}. Output only one word: 'positive' if
the tone is generally positive, 'negative' if the tone is generally negative, or 'neutral'
otherwise.""",
input_schema=None,
output_key="tone_check_result", # This agent's output determines the conditional flow
)
# --- Create the custom agent instance ---
story_flow_agent = StoryFlowAgent(
name="StoryFlowAgent",
story_generator=story_generator,
critic=critic,
reviser=reviser,
grammar_check=grammar_check,
tone_check=tone_check,
)
INITIAL_STATE = {"topic": "a brave kitten exploring a haunted house"}
# --- Setup Runner and Session ---
async def setup_session_and_runner():
session_service = InMemorySessionService()
session = await session_service.create_session(app_name=APP_NAME, user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID, state=INITIAL_STATE)
logger.info(f"Initial session state: {session.state}")
runner = Runner(
agent=story_flow_agent, # Pass the custom orchestrator agent
app_name=APP_NAME,
session_service=session_service
)
return session_service, runner
# --- Function to Interact with the Agent ---
async def call_agent_async(user_input_topic: str):
"""
Sends a new topic to the agent (overwriting the initial one if needed)
and runs the workflow.
"""
session_service, runner = await setup_session_and_runner()
current_session = session_service.sessions[APP_NAME][USER_ID][SESSION_ID]
current_session.state["topic"] = user_input_topic
logger.info(f"Updated session state topic to: {user_input_topic}")
content = types.Content(role='user', parts=[types.Part(text=f"Generate a story about the preset topic.")])
events = runner.run_async(user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID, new_message=content)
final_response = "No final response captured."
async for event in events:
if event.is_final_response() and event.content and event.content.parts:
logger.info(f"Potential final response from [{event.author}]: {event.content.parts[0].text}")
final_response = event.content.parts[0].text
print("\n--- Agent Interaction Result ---")
print("Agent Final Response: ", final_response)
final_session = await session_service.get_session(app_name=APP_NAME,
user_id=USER_ID,
session_id=SESSION_ID)
print("Final Session State:")
import json
print(json.dumps(final_session.state, indent=2))
print("-------------------------------\n")
# --- Run the Agent ---
# Note: In Colab, you can directly use 'await' at the top level.
# If running this code as a standalone Python script, you'll need to use asyncio.run() or manage the event loop.
await call_agent_async("a lonely robot finding a friend in a junkyard")
// Código ejecutable completo para el ejemplo de StoryFlowAgent
/**
* Copyright 2025 Google LLC
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
import {
LlmAgent,
BaseAgent,
LoopAgent,
SequentialAgent,
InMemoryRunner,
InvocationContext,
Event,
isFinalResponse,
} from '@google/adk';
import { createUserContent } from "@google/genai";
// --- Constants ---
const APP_NAME = "story_app_ts";
const USER_ID = "12345";
const SESSION_ID = "123344_ts";
const GEMINI_MODEL = "gemini-2.5-flash";
// --- Custom Orchestrator Agent ---
class StoryFlowAgent extends BaseAgent {
// --- Property Declarations for TypeScript ---
private storyGenerator: LlmAgent;
private critic: LlmAgent;
private reviser: LlmAgent;
private grammarCheck: LlmAgent;
private toneCheck: LlmAgent;
private loopAgent: LoopAgent;
private sequentialAgent: SequentialAgent;
constructor(
name: string,
storyGenerator: LlmAgent,
critic: LlmAgent,
reviser: LlmAgent,
grammarCheck: LlmAgent,
toneCheck: LlmAgent
) {
// Create internal composite agents
const loopAgent = new LoopAgent({
name: "CriticReviserLoop",
subAgents: [critic, reviser],
maxIterations: 2,
});
const sequentialAgent = new SequentialAgent({
name: "PostProcessing",
subAgents: [grammarCheck, toneCheck],
});
// Define the sub-agents for the framework to know about
const subAgentsList = [
storyGenerator,
loopAgent,
sequentialAgent,
];
// Call the parent constructor
super({
name,
subAgents: subAgentsList,
});
// Assign agents to class properties for use in the custom run logic
this.storyGenerator = storyGenerator;
this.critic = critic;
this.reviser = reviser;
this.grammarCheck = grammarCheck;
this.toneCheck = toneCheck;
this.loopAgent = loopAgent;
this.sequentialAgent = sequentialAgent;
}
// Implements the custom orchestration logic for the story workflow.
async* runLiveImpl(ctx: InvocationContext): AsyncGenerator<Event, void, undefined> {
yield* this.runAsyncImpl(ctx);
}
// Implements the custom orchestration logic for the story workflow.
async* runAsyncImpl(ctx: InvocationContext): AsyncGenerator<Event, void, undefined> {
console.log(`[${this.name}] Starting story generation workflow.`);
// 1. Initial Story Generation
console.log(`[${this.name}] Running StoryGenerator...`);
for await (const event of this.storyGenerator.runAsync(ctx)) {
console.log(`[${this.name}] Event from StoryGenerator: ${JSON.stringify(event, null, 2)}`);
yield event;
}
// Check if the story was generated before proceeding
if (!ctx.session.state["current_story"]) {
console.error(`[${this.name}] Failed to generate initial story. Aborting workflow.`);
return; // Stop processing
}
console.log(`[${this.name}] Story state after generator: ${ctx.session.state['current_story']}`);
// 2. Critic-Reviser Loop
console.log(`[${this.name}] Running CriticReviserLoop...`);
for await (const event of this.loopAgent.runAsync(ctx)) {
console.log(`[${this.name}] Event from CriticReviserLoop: ${JSON.stringify(event, null, 2)}`);
yield event;
}
console.log(`[${this.name}] Story state after loop: ${ctx.session.state['current_story']}`);
// 3. Sequential Post-Processing (Grammar and Tone Check)
console.log(`[${this.name}] Running PostProcessing...`);
for await (const event of this.sequentialAgent.runAsync(ctx)) {
console.log(`[${this.name}] Event from PostProcessing: ${JSON.stringify(event, null, 2)}`);
yield event;
}
// 4. Tone-Based Conditional Logic
const toneCheckResult = ctx.session.state["tone_check_result"] as string;
console.log(`[${this.name}] Tone check result: ${toneCheckResult}`);
if (toneCheckResult === "negative") {
console.log(`[${this.name}] Tone is negative. Regenerating story...`);
for await (const event of this.storyGenerator.runAsync(ctx)) {
console.log(`[${this.name}] Event from StoryGenerator (Regen): ${JSON.stringify(event, null, 2)}`);
yield event;
}
} else {
console.log(`[${this.name}] Tone is not negative. Keeping current story.`);
}
console.log(`[${this.name}] Workflow finished.`);
}
}
// --- Define the individual LLM agents ---
const storyGenerator = new LlmAgent({
name: "StoryGenerator",
model: GEMINI_MODEL,
instruction: `You are a story writer. Write a short story (around 100 words), on the following topic: {topic}`,
outputKey: "current_story",
});
const critic = new LlmAgent({
name: "Critic",
model: GEMINI_MODEL,
instruction: `You are a story critic. Review the story provided: {{current_story}}. Provide 1-2 sentences of constructive criticism
on how to improve it. Focus on plot or character.`,
outputKey: "criticism",
});
const reviser = new LlmAgent({
name: "Reviser",
model: GEMINI_MODEL,
instruction: `You are a story reviser. Revise the story provided: {{current_story}}, based on the criticism in
{{criticism}}. Output only the revised story.`,
outputKey: "current_story", // Overwrites the original story
});
const grammarCheck = new LlmAgent({
name: "GrammarCheck",
model: GEMINI_MODEL,
instruction: `You are a grammar checker. Check the grammar of the story provided: {current_story}. Output only the suggested
corrections as a list, or output 'Grammar is good!' if there are no errors.`,
outputKey: "grammar_suggestions",
});
const toneCheck = new LlmAgent({
name: "ToneCheck",
model: GEMINI_MODEL,
instruction: `You are a tone analyzer. Analyze the tone of the story provided: {current_story}. Output only one word: 'positive' if
the tone is generally positive, 'negative' if the tone is generally negative, or 'neutral'
otherwise.`,
outputKey: "tone_check_result",
});
// --- Create the custom agent instance ---
const storyFlowAgent = new StoryFlowAgent(
"StoryFlowAgent",
storyGenerator,
critic,
reviser,
grammarCheck,
toneCheck
);
const INITIAL_STATE = { "topic": "a brave kitten exploring a haunted house" };
// --- Setup Runner and Session ---
async function setupRunnerAndSession() {
const runner = new InMemoryRunner({
agent: storyFlowAgent,
appName: APP_NAME,
});
const session = await runner.sessionService.createSession({
appName: APP_NAME,
userId: USER_ID,
sessionId: SESSION_ID,
state: INITIAL_STATE,
});
console.log(`Initial session state: ${JSON.stringify(session.state, null, 2)}`);
return runner;
}
// --- Function to Interact with the Agent ---
async function callAgent(runner: InMemoryRunner, userInputTopic: string) {
const currentSession = await runner.sessionService.getSession({
appName: APP_NAME,
userId: USER_ID,
sessionId: SESSION_ID
});
if (!currentSession) {
return;
}
// Update the state with the new topic for this run
currentSession.state["topic"] = userInputTopic;
console.log(`Updated session state topic to: ${userInputTopic}`);
let finalResponse = "No final response captured.";
for await (const event of runner.runAsync({
userId: USER_ID,
sessionId: SESSION_ID,
newMessage: createUserContent(`Generate a story about: ${userInputTopic}`)
})) {
if (isFinalResponse(event) && event.content?.parts?.length) {
console.log(`Potential final response from [${event.author}]: ${event.content.parts.map(part => part.text ?? '').join('')}`);
finalResponse = event.content.parts.map(part => part.text ?? '').join('');
}
}
const finalSession = await runner.sessionService.getSession({
appName: APP_NAME,
userId: USER_ID,
sessionId: SESSION_ID
});
console.log("\n--- Agent Interaction Result ---");
console.log("Agent Final Response: ", finalResponse);
console.log("Final Session State:");
console.log(JSON.stringify(finalSession?.state, null, 2));
console.log("-------------------------------\n");
}
// --- Run the Agent ---
async function main() {
const runner = await setupRunnerAndSession();
await callAgent(runner, "a lonely robot finding a friend in a junkyard");
}
main();
# Código ejecutable completo para el ejemplo de StoryFlowAgent
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"iter"
"log"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent/workflowagents/loopagent"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent/workflowagents/sequentialagent"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent/llmagent"
"google.golang.org/adk/model/gemini"
"google.golang.org/adk/runner"
"google.golang.org/adk/session"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
// StoryFlowAgent is a custom agent that orchestrates a story generation workflow.
// It encapsulates the logic of running sub-agents in a specific sequence.
type StoryFlowAgent struct {
storyGenerator agent.Agent
revisionLoopAgent agent.Agent
postProcessorAgent agent.Agent
}
// NewStoryFlowAgent creates and configures the entire custom agent workflow.
// It takes individual LLM agents as input and internally creates the necessary
// workflow agents (loop, sequential), returning the final orchestrator agent.
func NewStoryFlowAgent(
storyGenerator,
critic,
reviser,
grammarCheck,
toneCheck agent.Agent,
) (agent.Agent, error) {
loopAgent, err := loopagent.New(loopagent.Config{
MaxIterations: 2,
AgentConfig: agent.Config{
Name: "CriticReviserLoop",
SubAgents: []agent.Agent{critic, reviser},
},
})
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to create loop agent: %w", err)
}
sequentialAgent, err := sequentialagent.New(sequentialagent.Config{
AgentConfig: agent.Config{
Name: "PostProcessing",
SubAgents: []agent.Agent{grammarCheck, toneCheck},
},
})
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to create sequential agent: %w", err)
}
// The StoryFlowAgent struct holds the agents needed for the Run method.
orchestrator := &StoryFlowAgent{
storyGenerator: storyGenerator,
revisionLoopAgent: loopAgent,
postProcessorAgent: sequentialAgent,
}
// agent.New creates the final agent, wiring up the Run method.
return agent.New(agent.Config{
Name: "StoryFlowAgent",
Description: "Orchestrates story generation, critique, revision, and checks.",
SubAgents: []agent.Agent{storyGenerator, loopAgent, sequentialAgent},
Run: orchestrator.Run,
})
}
// Run defines the custom execution logic for the StoryFlowAgent.
func (s *StoryFlowAgent) Run(ctx agent.InvocationContext) iter.Seq2[*session.Event, error] {
return func(yield func(*session.Event, error) bool) {
// Stage 1: Initial Story Generation
for event, err := range s.storyGenerator.Run(ctx) {
if err != nil {
yield(nil, fmt.Errorf("story generator failed: %w", err))
return
}
if !yield(event, nil) {
return
}
}
// Check if story was generated before proceeding
currentStory, err := ctx.Session().State().Get("current_story")
if err != nil || currentStory == "" {
log.Println("Failed to generate initial story. Aborting workflow.")
return
}
// Stage 2: Critic-Reviser Loop
for event, err := range s.revisionLoopAgent.Run(ctx) {
if err != nil {
yield(nil, fmt.Errorf("loop agent failed: %w", err))
return
}
if !yield(event, nil) {
return
}
}
// Stage 3: Post-Processing
for event, err := range s.postProcessorAgent.Run(ctx) {
if err != nil {
yield(nil, fmt.Errorf("sequential agent failed: %w", err))
return
}
if !yield(event, nil) {
return
}
}
// Stage 4: Conditional Regeneration
toneResult, err := ctx.Session().State().Get("tone_check_result")
if err != nil {
log.Printf("Could not read tone_check_result from state: %v. Assuming tone is not negative.", err)
return
}
if tone, ok := toneResult.(string); ok && tone == "negative" {
log.Println("Tone is negative. Regenerating story...")
for event, err := range s.storyGenerator.Run(ctx) {
if err != nil {
yield(nil, fmt.Errorf("story regeneration failed: %w", err))
return
}
if !yield(event, nil) {
return
}
}
} else {
log.Println("Tone is not negative. Keeping current story.")
}
}
}
const (
modelName = "gemini-2.0-flash"
appName = "story_app"
userID = "user_12345"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
model, err := gemini.NewModel(ctx, modelName, &genai.ClientConfig{})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create model: %v", err)
}
// --- Define the individual LLM agents ---
storyGenerator, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "StoryGenerator",
Model: model,
Description: "Generates the initial story.",
Instruction: "You are a story writer. Write a short story (around 100 words) about a cat, based on the topic: {topic}",
OutputKey: "current_story",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create StoryGenerator agent: %v", err)
}
critic, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "Critic",
Model: model,
Description: "Critiques the story.",
Instruction: "You are a story critic. Review the story: {current_story}. Provide 1-2 sentences of constructive criticism on how to improve it. Focus on plot or character.",
OutputKey: "criticism",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create Critic agent: %v", err)
}
reviser, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "Reviser",
Model: model,
Description: "Revises the story based on criticism.",
Instruction: "You are a story reviser. Revise the story: {current_story}, based on the criticism: {criticism}. Output only the revised story.",
OutputKey: "current_story",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create Reviser agent: %v", err)
}
grammarCheck, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "GrammarCheck",
Model: model,
Description: "Checks grammar and suggests corrections.",
Instruction: "You are a grammar checker. Check the grammar of the story: {current_story}. Output only the suggested corrections as a list, or output 'Grammar is good!' if there are no errors.",
OutputKey: "grammar_suggestions",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create GrammarCheck agent: %v", err)
}
toneCheck, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "ToneCheck",
Model: model,
Description: "Analyzes the tone of the story.",
Instruction: "You are a tone analyzer. Analyze the tone of the story: {current_story}. Output only one word: 'positive' if the tone is generally positive, 'negative' if the tone is generally negative, or 'neutral' otherwise.",
OutputKey: "tone_check_result",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create ToneCheck agent: %v", err)
}
// Instantiate the custom agent, which encapsulates the workflow agents.
storyFlowAgent, err := NewStoryFlowAgent(
storyGenerator,
critic,
reviser,
grammarCheck,
toneCheck,
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create story flow agent: %v", err)
}
// --- Run the Agent ---
sessionService := session.InMemoryService()
initialState := map[string]any{
"topic": "a brave kitten exploring a haunted house",
}
sessionInstance, err := sessionService.Create(ctx, &session.CreateRequest{
AppName: appName,
UserID: userID,
State: initialState,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create session: %v", err)
}
userTopic := "a lonely robot finding a friend in a junkyard"
r, err := runner.New(runner.Config{
AppName: appName,
Agent: storyFlowAgent,
SessionService: sessionService,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create runner: %v", err)
}
input := genai.NewContentFromText("Generate a story about: "+userTopic, genai.RoleUser)
events := r.Run(ctx, userID, sessionInstance.Session.ID(), input, agent.RunConfig{
StreamingMode: agent.StreamingModeSSE,
})
var finalResponse string
for event, err := range events {
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("An error occurred during agent execution: %v", err)
}
for _, part := range event.Content.Parts {
// Accumulate text from all parts of the final response.
finalResponse += part.Text
}
}
fmt.Println("\n--- Agent Interaction Result ---")
fmt.Println("Agent Final Response: " + finalResponse)
finalSession, err := sessionService.Get(ctx, &session.GetRequest{
UserID: userID,
AppName: appName,
SessionID: sessionInstance.Session.ID(),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to retrieve final session: %v", err)
}
fmt.Println("Final Session State:", finalSession.Session.State())
}
# Código ejecutable completo para el ejemplo de StoryFlowAgent
import com.google.adk.agents.LlmAgent;
import com.google.adk.agents.BaseAgent;
import com.google.adk.agents.InvocationContext;
import com.google.adk.agents.LoopAgent;
import com.google.adk.agents.SequentialAgent;
import com.google.adk.events.Event;
import com.google.adk.runner.InMemoryRunner;
import com.google.adk.sessions.Session;
import com.google.genai.types.Content;
import com.google.genai.types.Part;
import io.reactivex.rxjava3.core.Flowable;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
public class StoryFlowAgentExample extends BaseAgent {
// --- Constants ---
private static final String APP_NAME = "story_app";
private static final String USER_ID = "user_12345";
private static final String SESSION_ID = "session_123344";
private static final String MODEL_NAME = "gemini-2.0-flash"; // Ensure this model is available
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(StoryFlowAgentExample.class.getName());
private final LlmAgent storyGenerator;
private final LoopAgent loopAgent;
private final SequentialAgent sequentialAgent;
public StoryFlowAgentExample(
String name, LlmAgent storyGenerator, LoopAgent loopAgent, SequentialAgent sequentialAgent) {
super(
name,
"Orchestrates story generation, critique, revision, and checks.",
List.of(storyGenerator, loopAgent, sequentialAgent),
null,
null);
this.storyGenerator = storyGenerator;
this.loopAgent = loopAgent;
this.sequentialAgent = sequentialAgent;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// --- Define the individual LLM agents ---
LlmAgent storyGenerator =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("StoryGenerator")
.model(MODEL_NAME)
.description("Generates the initial story.")
.instruction(
"""
You are a story writer. Write a short story (around 100 words) about a cat,
based on the topic: {topic}
""")
.inputSchema(null)
.outputKey("current_story") // Key for storing output in session state
.build();
LlmAgent critic =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("Critic")
.model(MODEL_NAME)
.description("Critiques the story.")
.instruction(
"""
You are a story critic. Review the story: {current_story}. Provide 1-2 sentences of constructive criticism
on how to improve it. Focus on plot or character.
""")
.inputSchema(null)
.outputKey("criticism") // Key for storing criticism in session state
.build();
LlmAgent reviser =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("Reviser")
.model(MODEL_NAME)
.description("Revises the story based on criticism.")
.instruction(
"""
You are a story reviser. Revise the story: {current_story}, based on the criticism: {criticism}. Output only the revised story.
""")
.inputSchema(null)
.outputKey("current_story") // Overwrites the original story
.build();
LlmAgent grammarCheck =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("GrammarCheck")
.model(MODEL_NAME)
.description("Checks grammar and suggests corrections.")
.instruction(
"""
You are a grammar checker. Check the grammar of the story: {current_story}. Output only the suggested
corrections as a list, or output 'Grammar is good!' if there are no errors.
""")
.outputKey("grammar_suggestions")
.build();
LlmAgent toneCheck =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("ToneCheck")
.model(MODEL_NAME)
.description("Analyzes the tone of the story.")
.instruction(
"""
You are a tone analyzer. Analyze the tone of the story: {current_story}. Output only one word: 'positive' if
the tone is generally positive, 'negative' if the tone is generally negative, or 'neutral'
otherwise.
""")
.outputKey("tone_check_result") // This agent's output determines the conditional flow
.build();
LoopAgent loopAgent =
LoopAgent.builder()
.name("CriticReviserLoop")
.description("Iteratively critiques and revises the story.")
.subAgents(critic, reviser)
.maxIterations(2)
.build();
SequentialAgent sequentialAgent =
SequentialAgent.builder()
.name("PostProcessing")
.description("Performs grammar and tone checks sequentially.")
.subAgents(grammarCheck, toneCheck)
.build();
StoryFlowAgentExample storyFlowAgentExample =
new StoryFlowAgentExample(APP_NAME, storyGenerator, loopAgent, sequentialAgent);
// --- Run the Agent ---
runAgent(storyFlowAgentExample, "a lonely robot finding a friend in a junkyard");
}
// --- Function to Interact with the Agent ---
// Sends a new topic to the agent (overwriting the initial one if needed)
// and runs the workflow.
public static void runAgent(StoryFlowAgentExample agent, String userTopic) {
// --- Setup Runner and Session ---
InMemoryRunner runner = new InMemoryRunner(agent);
Map<String, Object> initialState = new HashMap<>();
initialState.put("topic", "a brave kitten exploring a haunted house");
Session session =
runner
.sessionService()
.createSession(APP_NAME, USER_ID, new ConcurrentHashMap<>(initialState), SESSION_ID)
.blockingGet();
logger.log(Level.INFO, () -> String.format("Initial session state: %s", session.state()));
session.state().put("topic", userTopic); // Update the state in the retrieved session
logger.log(Level.INFO, () -> String.format("Updated session state topic to: %s", userTopic));
Content userMessage = Content.fromParts(Part.fromText("Generate a story about: " + userTopic));
// Use the modified session object for the run
Flowable<Event> eventStream = runner.runAsync(USER_ID, session.id(), userMessage);
final String[] finalResponse = {"No final response captured."};
eventStream.blockingForEach(
event -> {
if (event.finalResponse() && event.content().isPresent()) {
String author = event.author() != null ? event.author() : "UNKNOWN_AUTHOR";
Optional<String> textOpt =
event
.content()
.flatMap(Content::parts)
.filter(parts -> !parts.isEmpty())
.map(parts -> parts.get(0).text().orElse(""));
logger.log(Level.INFO, () ->
String.format("Potential final response from [%s]: %s", author, textOpt.orElse("N/A")));
textOpt.ifPresent(text -> finalResponse[0] = text);
}
});
System.out.println("\n--- Agent Interaction Result ---");
System.out.println("Agent Final Response: " + finalResponse[0]);
// Retrieve session again to see the final state after the run
Session finalSession =
runner
.sessionService()
.getSession(APP_NAME, USER_ID, SESSION_ID, Optional.empty())
.blockingGet();
assert finalSession != null;
System.out.println("Final Session State:" + finalSession.state());
System.out.println("-------------------------------\n");
}
private boolean isStoryGenerated(InvocationContext ctx) {
Object currentStoryObj = ctx.session().state().get("current_story");
return currentStoryObj != null && !String.valueOf(currentStoryObj).isEmpty();
}
@Override
protected Flowable<Event> runAsyncImpl(InvocationContext invocationContext) {
// Implements the custom orchestration logic for the story workflow.
// Uses the instance attributes assigned by Pydantic (e.g., self.story_generator).
logger.log(Level.INFO, () -> String.format("[%s] Starting story generation workflow.", name()));
// Stage 1. Initial Story Generation
Flowable<Event> storyGenFlow = runStage(storyGenerator, invocationContext, "StoryGenerator");
// Stage 2: Critic-Reviser Loop (runs after story generation completes)
Flowable<Event> criticReviserFlow = Flowable.defer(() -> {
if (!isStoryGenerated(invocationContext)) {
logger.log(Level.SEVERE,() ->
String.format("[%s] Failed to generate initial story. Aborting after StoryGenerator.",
name()));
return Flowable.empty(); // Stop further processing if no story
}
logger.log(Level.INFO, () ->
String.format("[%s] Story state after generator: %s",
name(), invocationContext.session().state().get("current_story")));
return runStage(loopAgent, invocationContext, "CriticReviserLoop");
});
// Stage 3: Post-Processing (runs after critic-reviser loop completes)
Flowable<Event> postProcessingFlow = Flowable.defer(() -> {
logger.log(Level.INFO, () ->
String.format("[%s] Story state after loop: %s",
name(), invocationContext.session().state().get("current_story")));
return runStage(sequentialAgent, invocationContext, "PostProcessing");
});
// Stage 4: Conditional Regeneration (runs after post-processing completes)
Flowable<Event> conditionalRegenFlow = Flowable.defer(() -> {
String toneCheckResult = (String) invocationContext.session().state().get("tone_check_result");
logger.log(Level.INFO, () -> String.format("[%s] Tone check result: %s", name(), toneCheckResult));
if ("negative".equalsIgnoreCase(toneCheckResult)) {
logger.log(Level.INFO, () ->
String.format("[%s] Tone is negative. Regenerating story...", name()));
return runStage(storyGenerator, invocationContext, "StoryGenerator (Regen)");
} else {
logger.log(Level.INFO, () ->
String.format("[%s] Tone is not negative. Keeping current story.", name()));
return Flowable.empty(); // No regeneration needed
}
});
return Flowable.concatArray(storyGenFlow, criticReviserFlow, postProcessingFlow, conditionalRegenFlow)
.doOnComplete(() -> logger.log(Level.INFO, () -> String.format("[%s] Workflow finished.", name())));
}
// Helper method for a single agent run stage with logging
private Flowable<Event> runStage(BaseAgent agentToRun, InvocationContext ctx, String stageName) {
logger.log(Level.INFO, () -> String.format("[%s] Running %s...", name(), stageName));
return agentToRun
.runAsync(ctx)
.doOnNext(event ->
logger.log(Level.INFO,() ->
String.format("[%s] Event from %s: %s", name(), stageName, event.toJson())))
.doOnError(err ->
logger.log(Level.SEVERE,
String.format("[%s] Error in %s", name(), stageName), err))
.doOnComplete(() ->
logger.log(Level.INFO, () ->
String.format("[%s] %s finished.", name(), stageName)));
}
@Override
protected Flowable<Event> runLiveImpl(InvocationContext invocationContext) {
return Flowable.error(new UnsupportedOperationException("runLive not implemented."));
}
}